 Esophageal cancer occurs in the esophagus (a hollow, muscular tube that carries food and drink to the stomach). This cancer mostly develops in the inner lining of the esophagus and may gradually spread to the lymph nodes and other organs.
Statistics
Esophageal cancer is mostly found in men than women. It is the 8th most common cancer around the world. Esophageal cancer is mostly found in older people aged more than 55.
Symptoms
A sore or lump on the lip or in the mouth
A white and/or red...
Learn More
Esophageal cancer occurs in the esophagus (a hollow, muscular tube that carries food and drink to the stomach). This cancer mostly develops in the inner lining of the esophagus and may gradually spread to the lymph nodes and other organs.
Statistics
Esophageal cancer is mostly found in men than women. It is the 8th most common cancer around the world. Esophageal cancer is mostly found in older people aged more than 55.
Symptoms
A sore or lump on the lip or in the mouth
A white and/or red...
Learn More
 Non-melanoma skin cancer affects more than 3 million Americans each year, making it the most common type of cancer. About 90 percent of non-melanoma skin cancers are associated with exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. The 4 types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell cancer, and melanoma. Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common form of skin cancer while squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common form of skin cancer.
Sta...
Learn More
Non-melanoma skin cancer affects more than 3 million Americans each year, making it the most common type of cancer. About 90 percent of non-melanoma skin cancers are associated with exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. The 4 types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell cancer, and melanoma. Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common form of skin cancer while squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common form of skin cancer.
Sta...
Learn More
 For almost 2% of cancer patients, the cancer is only found after it has spread to a secondary site. These cancers are called carcinoma of unknown primary site or cancer of unknown primary (CUP). The primary site at times is unidentifiable because the tumor may be very small, the body caused it to shrink, or it was unintentionally removed during surgery. These cancers could be adenocarcinoma, poorly differentiated carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or neuroendocrine carcinoma. The American Cance...
Learn More
For almost 2% of cancer patients, the cancer is only found after it has spread to a secondary site. These cancers are called carcinoma of unknown primary site or cancer of unknown primary (CUP). The primary site at times is unidentifiable because the tumor may be very small, the body caused it to shrink, or it was unintentionally removed during surgery. These cancers could be adenocarcinoma, poorly differentiated carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or neuroendocrine carcinoma. The American Cance...
Learn More
 Cancer in children can transpire anywhere in the body in the blood and lymph node systems, brain and spinal cord (central nervous system; CNS), kidneys, and other organs and tissues. The types of cancer that infect the young mostly belong to one of these categories; leukemia, brain and spinal cord tumors, neuroblastoma, Wilms tumor, lymphoma (including both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin), rhabdomyosarcoma, retinoblastoma, and bone cancer (including osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma).
Statistics1...
Learn More
Cancer in children can transpire anywhere in the body in the blood and lymph node systems, brain and spinal cord (central nervous system; CNS), kidneys, and other organs and tissues. The types of cancer that infect the young mostly belong to one of these categories; leukemia, brain and spinal cord tumors, neuroblastoma, Wilms tumor, lymphoma (including both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin), rhabdomyosarcoma, retinoblastoma, and bone cancer (including osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma).
Statistics1...
Learn More
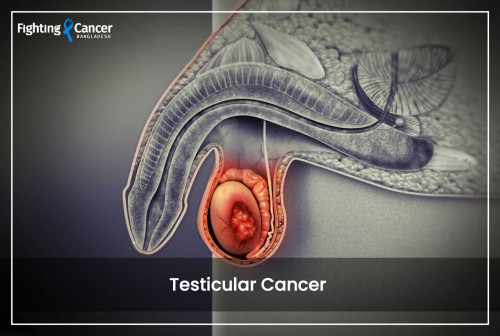 The testicles are two small, egg-shaped glands positioned close to the penis, with the scrotum—a loose skin —surrounding them. Testicles contain germ cells and other cells that make sperm and secrete testosterone. The origin of most testicular cancers is the sperm-producing germ cells, hence are referred to as germ cell tumors. The major categories of testicular cancers are germ cell tumors, stromal tumors, and carcinoma in situ of the testicle.
StatisticsTesticular cancer is rampan...
Learn More
The testicles are two small, egg-shaped glands positioned close to the penis, with the scrotum—a loose skin —surrounding them. Testicles contain germ cells and other cells that make sperm and secrete testosterone. The origin of most testicular cancers is the sperm-producing germ cells, hence are referred to as germ cell tumors. The major categories of testicular cancers are germ cell tumors, stromal tumors, and carcinoma in situ of the testicle.
StatisticsTesticular cancer is rampan...
Learn More