টিউমার হলো কিছু অস্বাভাবিক টিস্যুর সমাবেশ, যেখানে কোষগুলো অস্বাভাবিক প্রক্রিয়ায় সংখ্যা বৃদ্ধি করে। টিউমারগুলি হাড়, ত্বক, টিস্যু, অঙ্গ এবং গ্রন্থিগুলির ক্ষতি করতে পারে।
এটি একটি ভুল ধারণা যে সমস্ত টিউমারই ক্যান্সারে পরিনত হয়, তবে এটি সত্য নয়।
টিউমার ২ প্রকার হতে পারে। যথাঃ
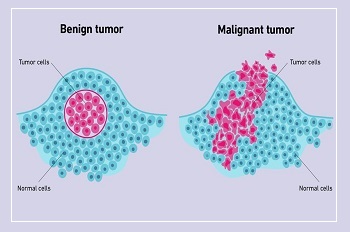
১. বেনাইন টিউমার ( ক্যান্সারমুক্ত টিউমার) যারা বিপজ্জনক নয়।
২.ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমার ( ক্যান্সারযুক্ত টিউমার) যারা বিপজ্জনক।
বেনাইন টিউমার যন্ত্রনাদায়ক এবং কিছুটা বিপজ্জনক হতে পারে, কিন্তু তারা ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমারের তুলনায় কম বিপজ্জনক ও কম ক্ষতিকর । বেনাইন টিউমার সাধারণত অন্য কোষকে আক্রমণ করে না বা ছড়িয়ে পড়ে না, অপরদিকে ম্যালিগন্যান্ট কোষগুলি শরীরের অন্যান্য অংশে ছড়িয়ে পড়ে ।
বেনাইন টিউমার:
বেনাইন টিউমার খুব কমই ক্ষেত্রেই মারাত্মক রূপ ধারণ করে। এগুলি বড় আকারে বাড়তে পারে এবং এর উপসর্গ অস্বস্তির কারণ হতে পারে, তবে এগুলিকে ক্যান্সার হিসাবে বিবেচনা করা হয় না কারণ তারা কাছাকাছি টিস্যুতে আক্রমণ করে না বা শরীরের অন্যান্য অংশে ছড়িয়ে পড়ে না।এ টিউমারের কারনে নানা রকম অস্বস্তি দেখা দিতে পারে, তবে এগুলি সাধারণত জীবন-হুমকিপূর্ণ নয় এবং প্রায়শই সাধারণ পদ্ধতি বা ওষুধ দিয়ে চিকিৎসাযোগ্য।
বেশিরভাগ বেনাইন টিউমারের চিকিৎসার প্রয়োজন হয় না। তবে কিছু বেনাইন টিউমার মারাত্মক ক্ষতি করতে পারে এবং এ ধরনের টিউমার গুলোর চিকিৎসার প্রয়োজন হয়।বেনাইন টিউমার অবস্থার কিছু সাধারণ উদাহরণের মধ্যে রয়েছে মোল, সিস্ট এবং ফাইব্রয়েড।বেনাইন টিউমার অবস্থার কিছু সাধারণ উদাহরণের মধ্যে রয়েছে মোল, সিস্ট এবং ফাইব্রয়েড।
বেনাইন টিউমার ক্যান্সারে পরিণত হওয়ার সম্ভাবনা:
কিছু বেনাইন টিউমারেরও ক্যান্সার হওয়ার সম্ভাবনা থাকে যখন টিউমার কোষগুলি নিয়ন্ত্রণহীন অস্বাভাবিক হারে সংখ্যাবৃদ্ধি করতে থাকে। এই ধরনের টিউমারগুলি নিবিড়ভাবে পর্যবেক্ষণ করা হয়।
বেনাইন টিউমারের কয়েকটি প্রকারভেদ :
১. অ্যাডেনোমাস
২. ফাইব্রোমাস
৩. ডেসময়েড টিউমার
৪. হ্যামারটোমাস
৫. হেম্যানজিওমাস
৬. লিপোমাস
৭. লিওমিওমাস
৮. মায়োমাস
৯. প্যাপিলোমাস
বেনাইন টিউমারের ঝুঁকির কারণগুলি:
১. মানসিক ও শারীরিকভাবে চাপে
২. খাদ্যাভ্যাস
৩. টিউমারের পারিবারিক ইতিহাস
৪. ঘন ঘন ইনফেকশনে সংক্রমিত হওয়া
বেনাইন টিউমারের চিকিৎসা (প্রয়োজনে):
বেনাইন টিউমারগুলি ধীরে ধীরে বৃদ্ধি পায় এবং সাধারণত এ টিউমারের কারনে অপারেশন বা অস্ত্রোপচার এর প্রয়োজন হয় না। এ টিউমার কাছাকাছি অঙ্গ বা স্নায়ুতে বংশবৃদ্ধি বা রক্তনালী বা মস্তিষ্ক বা মেরুদন্ডে অস্বাভাবিক হারে বৃদ্ধির মাধ্যমে গুরুতর স্বাস্থ্যঝুকি তৈরি করতে পারে। উপরোক্ত অঙ্গগুলোতে টিউমার দেখা দিলে অস্ত্রপচার করে অপসারণ করা প্রয়োজন। একবার অপসারণ করা হলে,বেশিরভাগক্ষেত্রেই বেনাইন টিউমার ফিরে আসে না।
ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমার :
ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমারকে ক্যান্সার টিউমারও বলা হয়। এ টিউমারের কোষ শরীরের অন্যান্য অংশে ছড়িয়ে পড়ে। ম্যালিগন্যান্ট বা ক্যান্সার টিউমার কাছাকাছি টিস্যু, গ্রন্থি এবং শরীরের অন্যান্য অংশে ছড়িয়ে পড়তে পারে। ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমারের প্রভাব খুব গুরুতর হতে পারে এবং দ্রুত চিকিৎসার প্রয়োজন হয়। এই টিউমারগুলি জীবনে হুমকিস্বরুপ ।
ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমার কয়েকটি প্রকার হলো :
*কার্সিনোমাস
*সারকোমাস
*সারকোমাস
*জীবাণু কোষ
*ব্লাস্টোমাস
ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমারের ঝুঁকির কারণগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে :
*ধূমপান
*অ্যালকোহল
*ক্যান্সারের পারিবারিক ইতিহাস
*টিউমারের ধরন
*কার্সিনোজেন এক্সপোজার
*জেনেটিক্স
*হিউম্যান প্যাপিলোমা ভাইরাস (এইচপিভি)
*স্থূলতা
*অতিরিক্ত ওজন
চিকিৎসা :
ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমার দ্রুত দেহে ছড়িয়ে পড়ে এবং পরবর্তীতে ক্যান্সারের পরিণত হয়। সার্জারি, রেডিয়েশন থেরাপি বা কেমোথেরাপির মাধ্যমে এ টিউমার অপসারণ করা হয় । ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমার চিকিৎসার পরও ফিরে আসতে পারে।
টিউবারকিউলোসিস:
টিউবারকিউলোসিস বা টিবি,একটি সংক্রামক রোগ যা ব্যাকটেরিয়ার সংক্রমনে হয়। এটি প্রাথমিকভাবে ফুসফুসকে প্রভাবিত করে তবে শরীরের অন্যান্য অংশকেও প্রভাবিত করতে পারে। টিবি এবং ক্যান্সার দুটি ভিন্ন রোগ যা মানবদেহকে ভিন্ন উপায়ে প্রভাবিত করে। তবে কিছু নির্দিষ্ট লক্ষনে মিল থাকায় টিবি এবং ক্যান্সারের মধ্যে কিছু বিভ্রান্তি সৃষ্টি হতে পারে ।
টিউবারকিউলোসিস এবং টিউমার বা ক্যান্সারের মধ্যে বিভ্রান্তি সৃষ্টি হওয়ার অন্যতম কারণ হলো টিবি ফুসফুসে নোডুলস বা ছোট পিণ্ড তৈরি করতে পারে।
এই নোডুলগুলিকে গ্রানুলোমাস বলা হয় যাদেখতে অনেকটা ক্যান্সারের টিউমারের মতো মনে হয় এক্স-রে বা সিটি স্ক্যানসহ বিভিন্ন ইমেজিং পরীক্ষায়। যদিও গ্রানুলোমাস টিউমার নয় কারণ এগুলো কোষের অনিয়ন্ত্রিত বৃদ্ধির ফলে তৈরি হয় না।
আবার, টিবি ফুসফুসে দাগ সৃষ্টি করতে পারে, যা কখনও কখনও এক্স-রে বা সিটি স্ক্যানে টিউমার এর মত মনে হতে পারে। তবে টিউবারকিউলোসিস কোনো টিউমার নয়।
একজন অভিজ্ঞ ডাক্তার সহজেই রোগীর চিকিৎসা ইতিহাস, লক্ষণ এবং ডায়াগনস্টিক পরীক্ষা সহ বিভিন্ন লক্ষনের উপর ভিত্তি করে টিবি এবং টিউমারের মধ্যে পার্থক্য করতে পারবেন।
টিবি অ্যান্টিবায়োটিক দিয়ে চিকিৎসাযোগ্য, অন্যদিকে ক্যান্সারের জন্য আরও জটিল চিকিৎসা যেমন সার্জারি, কেমোথেরাপি বা রেডিয়েশন থেরাপির প্রয়োজন হতে পারে।
বলা যায়, বেনাইন, ম্যালিগন্যান্ট এবং টিউবারকুলোসিস সবগুলি ভিন্ন ধরনের মেডিকেল কন্ডিশন যা শরীরে ভিন্নভিন্ন প্রভাব ফেলতে পারে। বেনাইন টিউমার ক্যান্সার নয় এবং শরীরের অন্যান্য অংশে ছড়ায় না, যেখানে ম্যালিগন্যান্ট টিউমার সমস্যা ক্যান্সারজনিত এবং ছড়াতে পারে। টিউবারকুলোসিস একটি ব্যাকটেরিয়াল সংক্রমণ যা অত্যন্ত সংক্রমণশীল হতে পারে এবং প্রাথমিকভাবে ফুসফুসে প্রভাব ফেলে।


